5 min read
— views•Building a Modern Data Warehouse with AWS Glue, Athena, and S3
Building a Modern Data Warehouse with AWS Glue, Athena, and S3
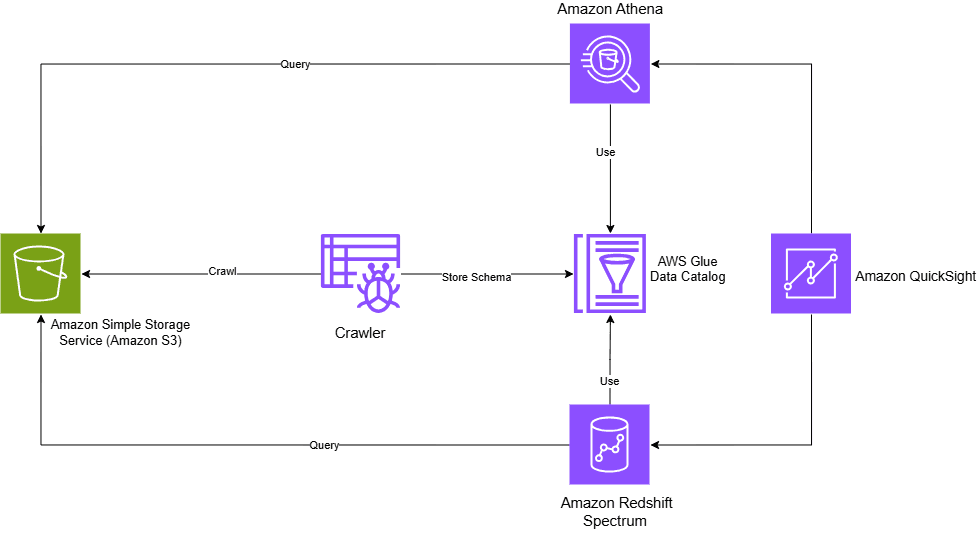
Why This Architecture Matters
In today's data-driven landscape, organizations need storage solutions that are both secure and efficient. The challenge? Managing massive datasets while keeping costs down and maintaining fast query performance.
Here's the solution I'd build again without hesitation: a proper lakehouse setup that's affordable, scalable, and teaches you the fundamentals of modern data platforms.
#The Core ConceptYour data lives in S3, but you query it as if it's in a traditional data warehouse. No loading into Redshift. No massive processing jobs. Just structured data with fast, cost-effective access.
The stack:
- Amazon S3 for data storage
- AWS Glue to catalog and organize metadata
- Amazon Athena (or Redshift Spectrum) for SQL queries
- QuickSight for visualization
This architecture is becoming the new standard for modern data platforms. Let me show you why.
Understanding the Components
#Amazon S3: The FoundationAmazon S3 is the backbone of this architecture. It's an object storage service designed to handle any data type—CSV files, JSON, Parquet, images, videos, and more.
Key features:
- Durability: 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability
- Scalability: Store unlimited data without capacity planning
- Flexibility: Multiple storage classes for different access patterns
- S3 Standard: Frequently accessed data
- S3 Glacier Deep Archive: Long-term archival (accessed 1-2x yearly)
- And many options in between
Pricing model:
- Inbound transfers: Free
- Outbound transfers: Tiered pricing (cost decreases with volume)
- Pay only for what you use
AWS Glue is a fully managed, serverless ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) service that makes data integration seamless.
Core components:
1. Glue Data Catalog
The Data Catalog is your metadata repository—think of it as a centralized schema registry. It stores:
- Table schemas and column definitions
- S3 locations and partition information
- Table properties and statistics
Important: The Data Catalog stores metadata about your data, not the data itself.
2. Glue Crawlers
Crawlers are automated processes that:
- Scan your data sources (S3, DynamoDB, JDBC databases)
- Automatically infer schemas
- Populate the Data Catalog with discovered metadata
- Can be scheduled to detect new data or schema changes
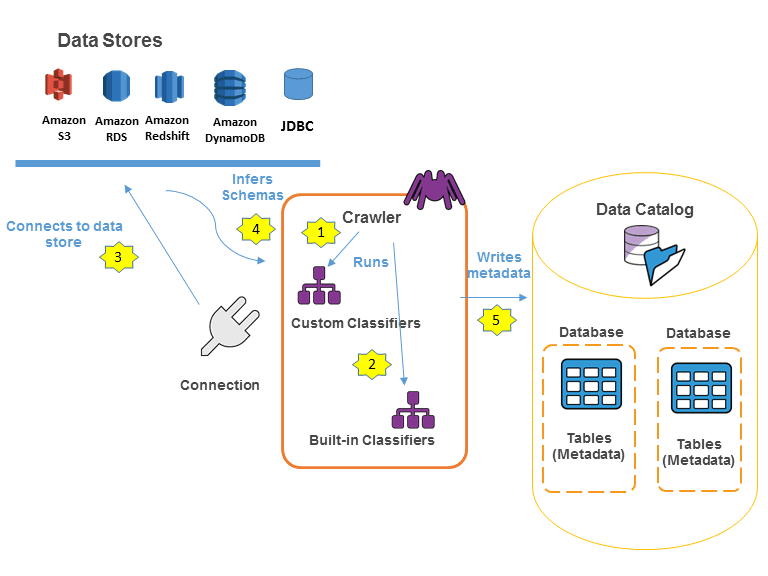
Pricing: Serverless model—you only pay for resources consumed while jobs or crawlers are running.
#Amazon Athena: The Query EngineAthena is a serverless, interactive query service that lets you analyze data directly in S3 using standard SQL. No infrastructure to manage, no data to load.
Perfect for:
- Ad-hoc data exploration
- Log analysis
- Business intelligence queries
- Quick data validation
Redshift Spectrum extends Amazon Redshift to query data in S3 without loading it into the cluster. This gives you:
- The power of Redshift's query optimizer
- Direct access to your data lake
- Flexibility to keep hot data in Redshift and cold data in S3
Hands-On: Building Your Lakehouse
#Prerequisites- AWS account with appropriate IAM permissions
- Data stored in S3 (or follow along with the streaming example below)
For this example, I'm using a Kafka streaming pipeline that continuously writes data to S3:
Architecture flow:
- Kafka Producer generates data
- Kafka Consumer reads messages
- Consumer writes to S3 every second
Create your S3 bucket:
# Bucket name: data-stream-kafka
Once your pipeline is running, data flows continuously into S3:
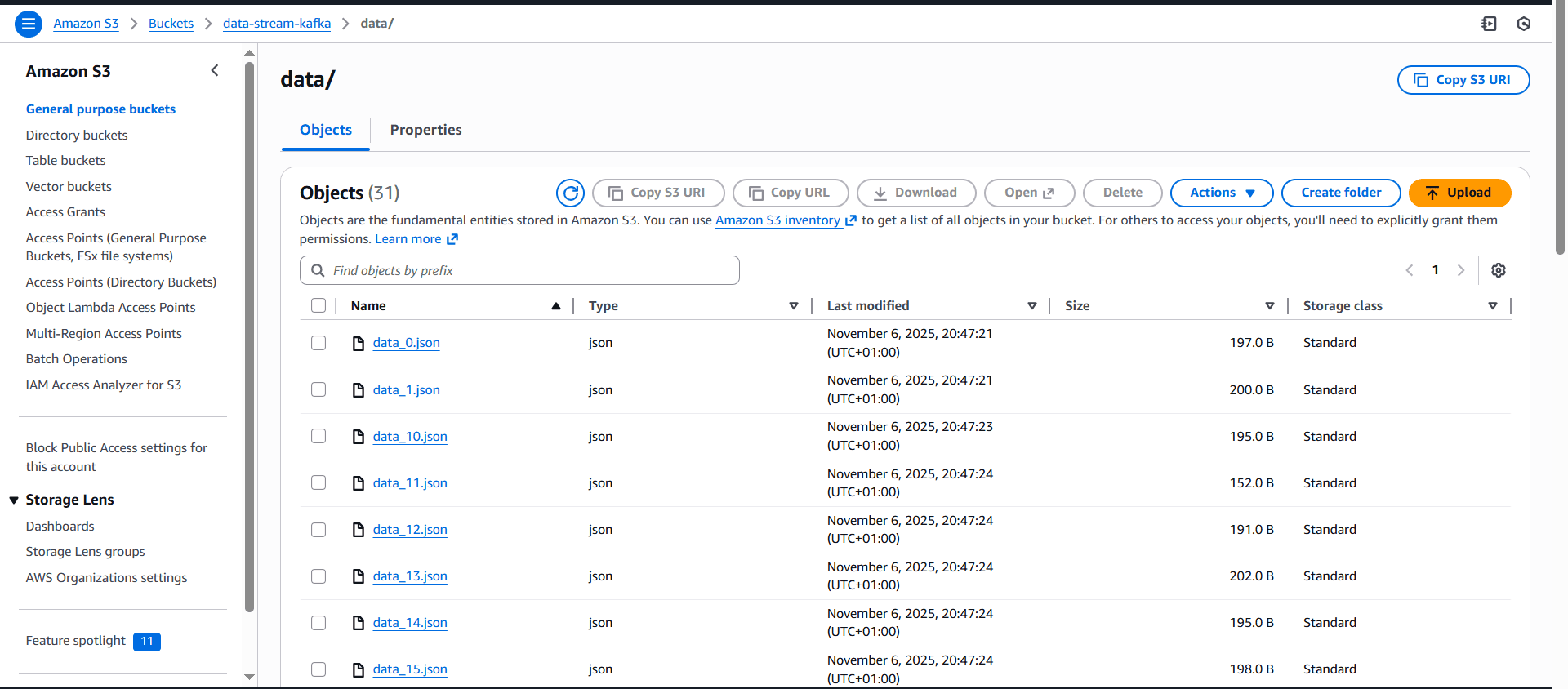
Navigate to AWS Glue Console and create a new database:
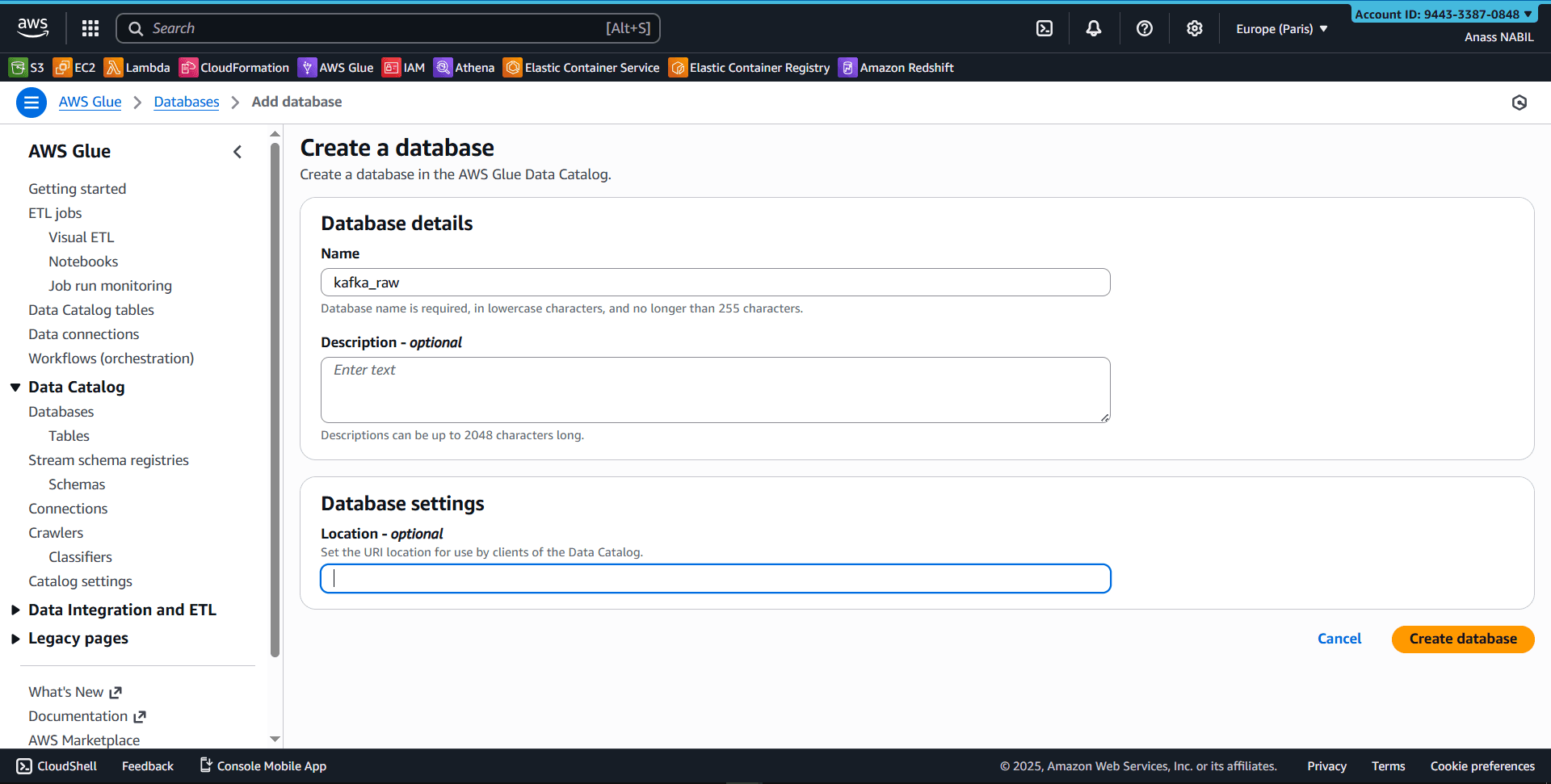
- Create a new crawler (e.g.,
kafka_crawler) - Select S3 as data source
- Critical: Add a trailing slash to your S3 path
- ✅ Correct:
s3://your-bucket-name/your-data-folder/ - ❌ Incorrect:
s3://your-bucket-name/your-data-folder
- ✅ Correct:
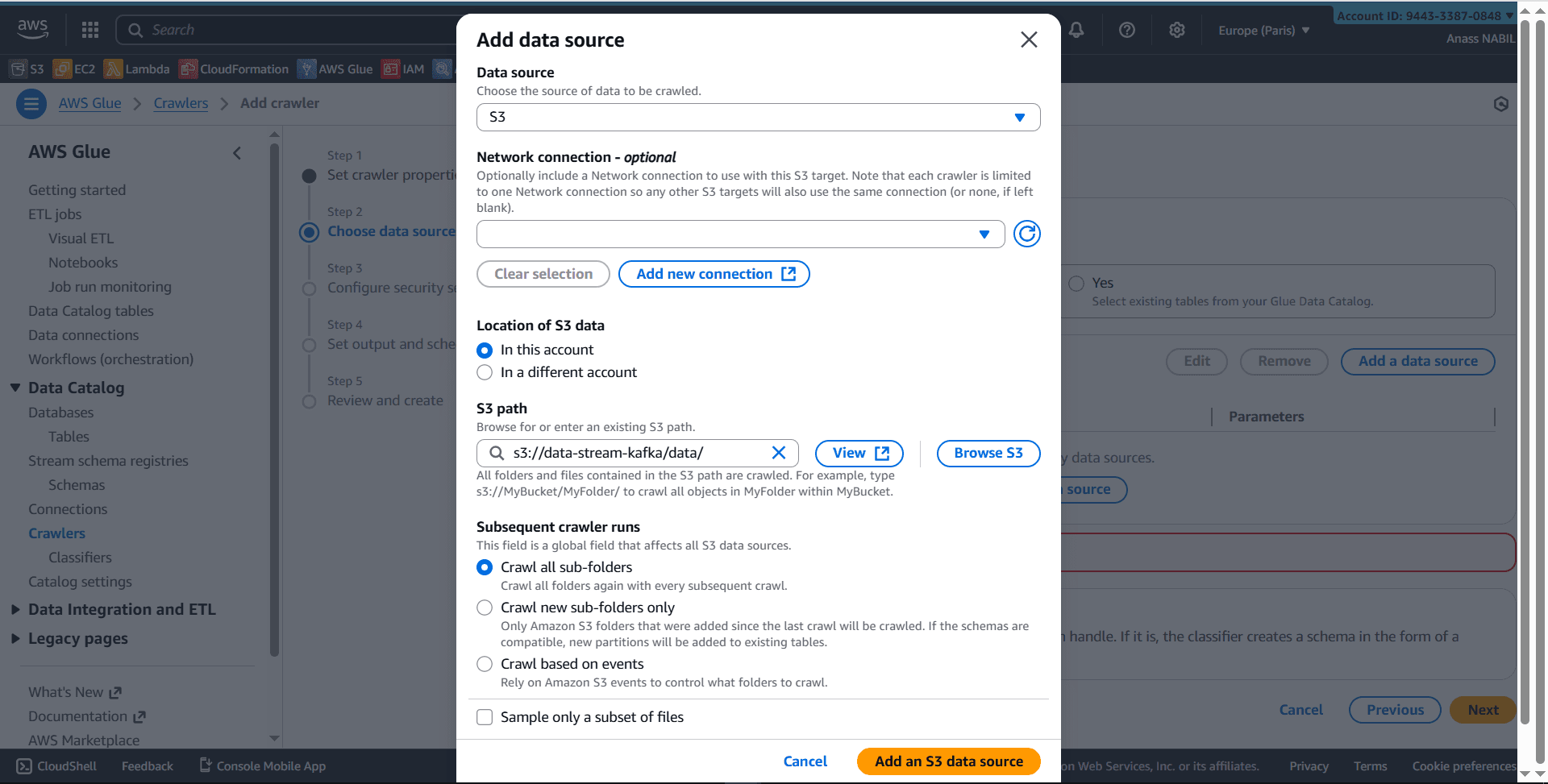
- Run the crawler
The crawler will:
- Scan your S3 bucket
- Infer the schema automatically
- Create/update tables in the Glue Data Catalog
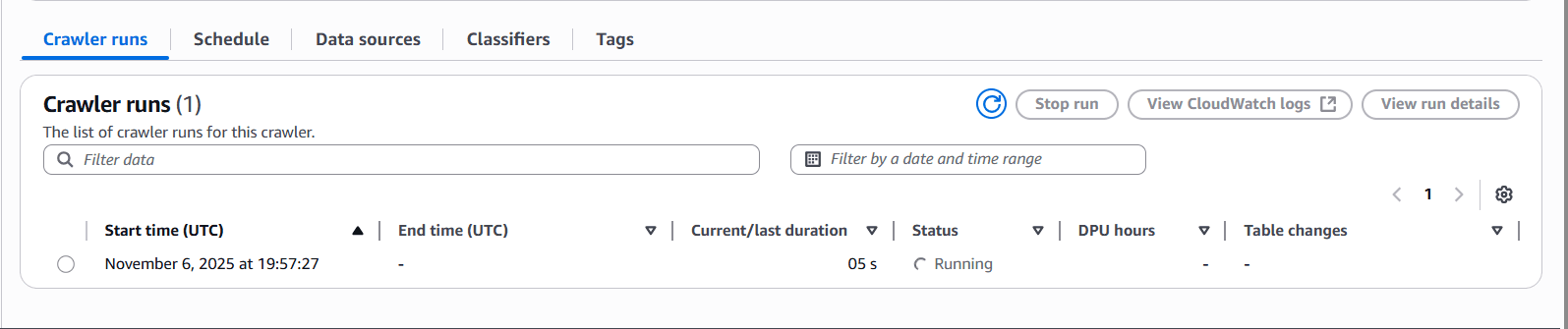
- Verify the results in the Glue Console's table section
First-time setup:
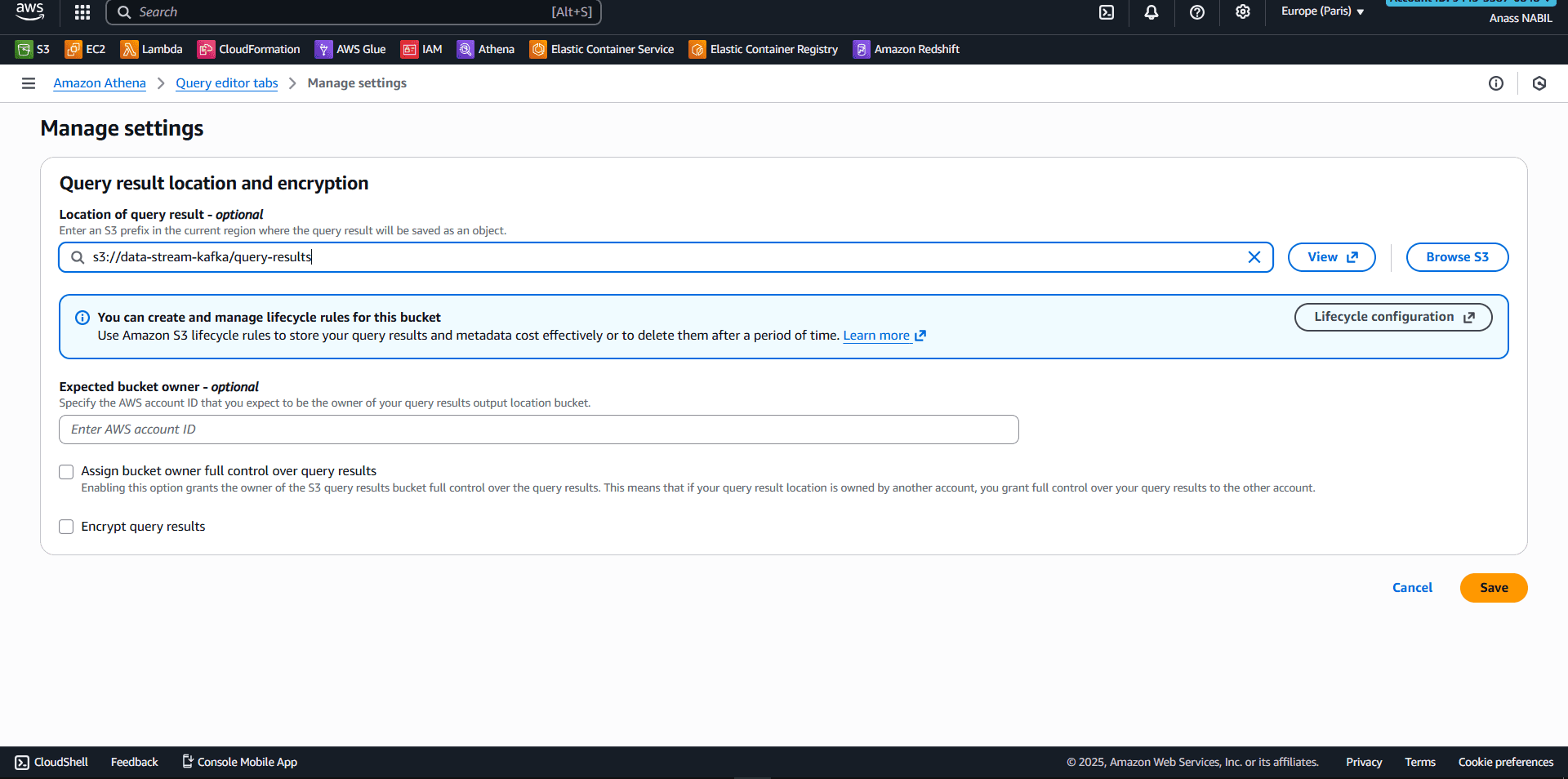
- Open Amazon Athena console
- Click Manage → Settings
- Specify S3 location for query results
- Example:
s3://my-s3-bucket/query-results/
- Example:
Run your first query:
SELECT *
FROM "kafka_raw"."data"
LIMIT 10;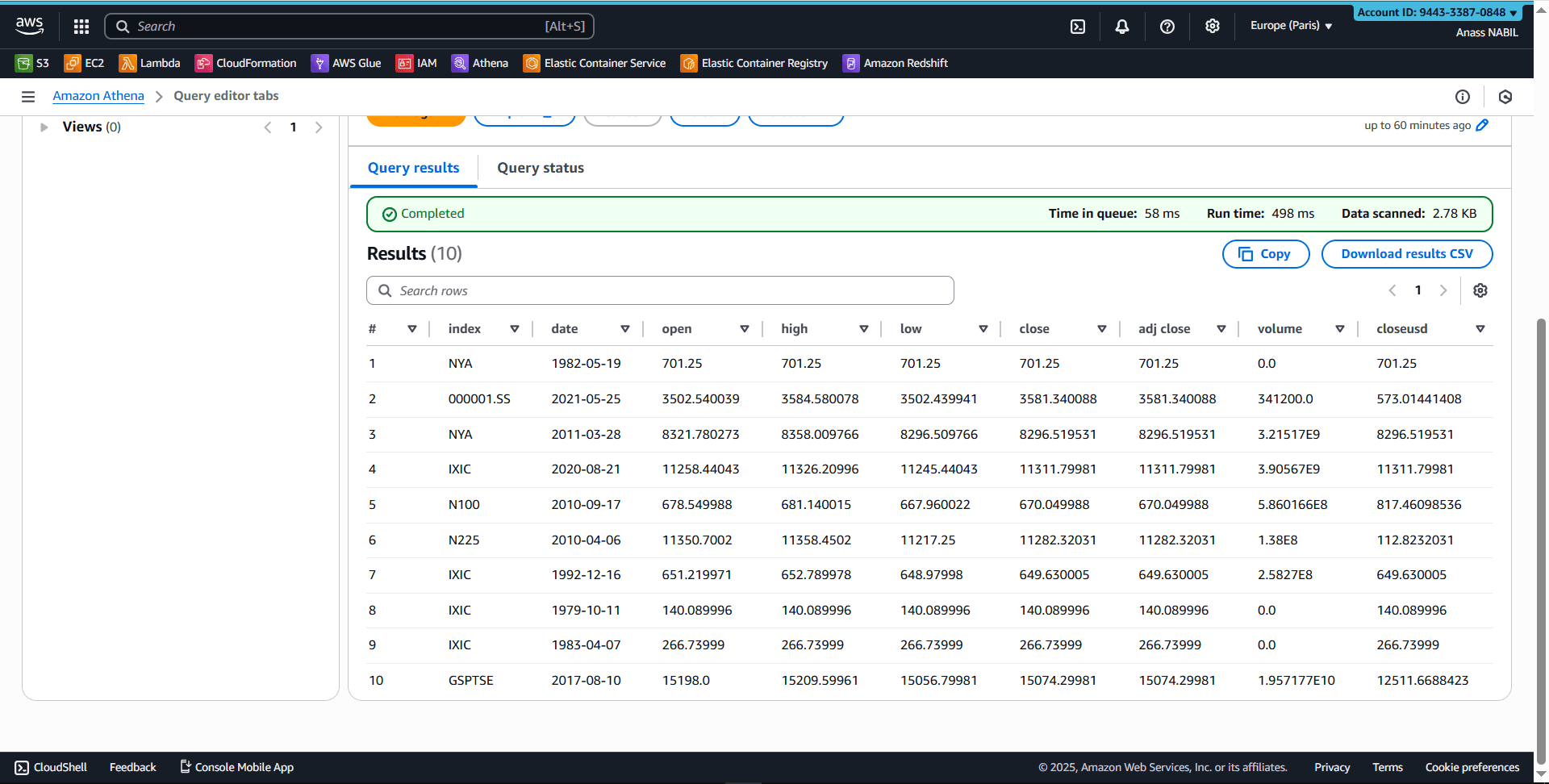
And that's it! You're now querying data stored in S3 using standard SQL, with the Glue Data Catalog providing schema management.
Key Takeaways
✅ No data movement: Query directly from S3 without loading data
✅ Serverless: No infrastructure to manage or provision
✅ Cost-effective: Pay only for queries run and data scanned
✅ Scalable: Handle petabytes of data without architectural changes
✅ Modern standard: This lakehouse pattern is becoming industry-standard
Why This Matters for Your Career
Building this architecture demonstrates you understand:
- Modern data platform design
- Serverless data engineering
- Cost optimization strategies
- The shift from traditional warehouses to lakehouse architectures
If you want to show you get modern data platforms, this is the project to build.
Enjoy this post? Like and share!